LOW-E glass, whose full Chinese name is “LOW-Emissivity glass”. It is a special type of glass formed by coating one or more layers of extremely thin metal or metal oxide films on the surface of ordinary glass.
Emissivity refers to the ability of an object’s surface to radiate thermal energy. The emissivity of ordinary glass is very high (about 0.84), which means it absorbs a large amount of heat and radiates it back in the form of long-wave infrared rays. The special film layer of LOW-E glass has an extremely LOW surface emissivity (as low as below 0.15), which means it can significantly reduce the radiation loss of heat energy, thereby providing excellent thermal insulation and heat preservation effects.
The working principle of the LOW-E film layer can be vividly understood as a “heat-selective mirror”.
1.Allow visible light to pass through: It has a high transmittance for visible light, ensuring sufficient indoor lighting and good transparency.
2.Reflecting far-infrared thermal radiation: It has a very high reflectivity for far-infrared rays with longer wavelengths (that is, the heat we usually sense).
In winter, the heat generated by indoor heating, human bodies and electrical appliances will attempt to escape to the outside in the form of glass can reflect this part of the heat back into the room, reducing heat loss and keeping the room warm.
In summer, when the heat from the outdoor sunlight (including far-infrared radiation) attempts to enter the room, LOW-E glass can reflect it back, reducing the heat entry and keeping the room cool.
Attention: The energy in sunlight mainly consists of three parts: visible light, near-infrared rays (which bring heat), and ultraviolet rays (which causes things to fade).
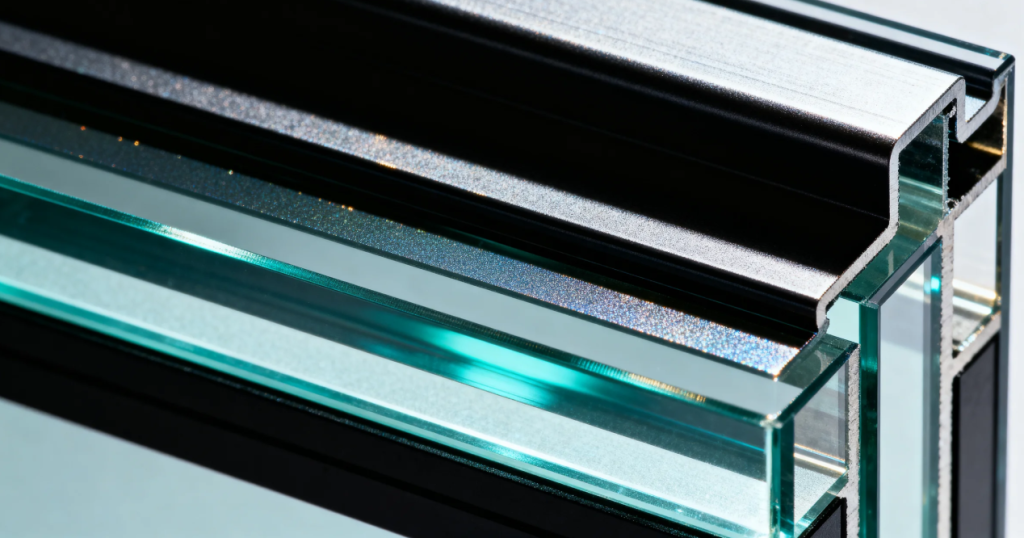
According to the performance characteristics and manufacturing processed of the film layer, LOW-E glass is mainly divided into two categories:
1.Offline higgh-transparency LOW-E glass: It has an extremely high visible light transmittance (good light transmittance, brighter indoor space), and can effectively reflect far-infrared thermal radiation at the same time.
Advantages: The prominent advantages are natural lighting and excellent heat preservation and insulation performance. It is highly suitable for use in cold regions. In winter, it can maximize the utilization of sunlight’s heat (“passive solar heat gain”) while preventing indoor heat from escaping.
Disadvantages: The film layer is rather fragile and must be used as insulating glass. It cannot be used alone or exposed to the air.
2.Online sunshade type LOW-E glass (also known as “tempered LOW-E”)
Characteristic: While ensuring a certain visible light transmittance, it places more emphasis on the shielding effect against solar thermal radiation. It can reflect more near-infrared rays (heat) in sunlight.
Advantages: The film layer is hard and durable, and can undergo deep processing such as tempering and lamination like ordinary glass, making its application more flexible. It is suitable for use in hot regions or on the west-facing sides of buildings with high shading requirements, such as glass curtain walls, and can effectively reduce the energy consumption of air conditioning cooling.
Disadvantages: Copared with offline LOW-E, its heat insulation performance is usually slightly inferior.
Keep warm in winter: Reducing the radiation loss of indoor heat through glass to the outside can lower heating energy consumption by more than 30%.
Summer heat insulation: Reflecting the solar heat energy from outside can reduce the energy consumption of air conditioning cooling by more than 30%.
Improve comfort: Reduce the sense of “cold radiation” or “hot radiation” near the glass to make the indoor temperature more uniform and make people feel more comfortable. When approcaching the window, one won’t feel a distinct cold or heat.
Protecting indoor items: LOW-E glass can reflect the vast majority (over 90%) of harmful ultraviolet rays, effectively slowing down the fading and aging of indoor furniture, carpets, artworks, curtains and other items.
Optical performance is controllable: By adjusting the film layer, LOW-E glass different light transmittance and colors (such as colorless, blue, gray,etc.) can be produced to meet the requirements of architectural aesthetics and lighting.
Application: Widely used in almost all buildings that require energy conservation and comfort, such as doors and windows of high-end residences; Glass curtain walls of commercial buildings; Large pubic buildings (airports, stations, stadiums); Cold storage.
LOW-E glass is a high-tech energy-saving glass that significantly reduces thermal radiation conduction by coating a special film layer on its surface. It is like putting a pair of “smart contact lenses” on the glass, which can not only ensure sufficient indoor light but also keep it warm in winter and cool in summer. It is the preferred material for modern green buildings and energy-saving doors and windows.
















Methods for distinguishing Indoor and Outdoor Aluminium Doors


Maintenance methods and tips for aluminium doors and windows

Characteristic of outward-opening and hung aluminium windows

Xinhe Aluminium Research: 7.14-7.18 Analysis of Aluminium Prices



Seven Benefits Of Using Aluminium Profiles In Curtain Wall Systems



The Application of Aluminium Profiles in New Energy Vehicles

The Composition and Application of Series 6 Aluminium Alloys


Top 5 Benefits of Using LED Aluminium Profiles in Modern Lighting

A Complete Guide to Aluminium Frame Profiles for Modern Structures



Exploring the Strength and Versatility of Aluminium Extrusion Profiles

How to Choose the Right Aluminium Profile Supplier for Your Project
