Application components: door frames, roof longitudinal beams, A/B/C columns, anti-collision beams, floor beams, etc.
Advantage–The weight reduction effect is remarkable: The density of aluminium is only one-third that of steel, which can reduce the overall vehicle weight by 10% to 20% and increase the driving range by 5% to 10%.
Good energy absorption: the crumb energy absorption property of aluminium alloy enhances collision safety (for example, the Tesla Mode S adopts an all-aluminium body)
Typical process: extruded aluminium profiles (6000 and 7000 series alloys) are used in frame structures, such as the “aluminium extruded threshold beam” of NIO ET7
Die-cast aluminium + profile combination: the Tesla Model Y adopts an integrated die-cast rear base plate, combined with aluminium profile reinforcing parts, to reduce welding points.
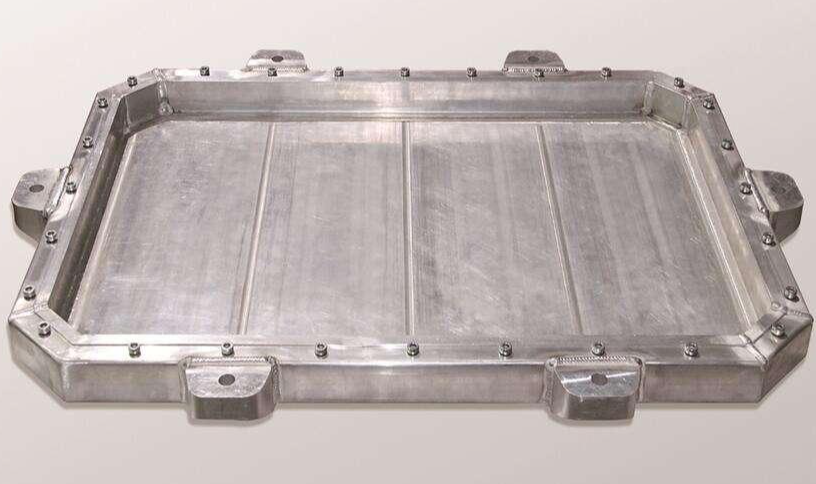
Application components: battery pack housing, battery tray, module bracket, cooling system
Advantage–Lightweight: aluminium battery packs are over 30% lighter than steel ones, enhancing energy density.
Thermal management: aluminium profile integrated liquid cooling channel (such as the aluminium tray of BYD Blade Battery)
Anti-corrosion: surface treatment (anodizing, spraying) enhances the resistance to electrolyte corrosion.
Typical process–high-strength 6xxx series aluminium profiles: used for battery pack frames, requiring impact resistance (such as CATL’S CTP technology)
Extrusion + welding process: aluminium profiles are spliced into battery trays, which has a cost advantage over die-cast parts.
Application components: motor housing, inverter bracket, reducer housing.
Advantage– Good heat dissipation: aluminium has a high thermal conductivity (about 200W/m·K), which is suitable for the heat dissipation requirements of motors.
Vibration and noise reduction: aluminium alloy can reduce the high-frequency vibration noise of the motor.
Typical process–Extruded aluminium profiles + CNC processing: used for motor housings, such as the asynchronous motor housing of Xiaopeng P7.
Thin-walled complex profiles: used for inverter cooling water channels (wall thickness can be less than 2mm).

Application components: Sub-frame, control arm, steering knuckle
Advantage–Reduce unsprung mass: aluminium suspension components are 40% lighter than steel ones,enhancing handling.
Fatigue resistance: forged aluminium profiles (such as 6082-T6) are used for high-stress components.
Material innovation–High-strength aluminium alloys: 7000 series (such as 7055), aluminium-lithium alloys (with a weight reduction of over 10%) are used for key structural components.
Recycled aluminium application–Tesla plans to use 50% recycled aluminium in the battery tray of the Cybertruck
Process upgrade– Integrated die-casting + profile composite structure: Tesla’s “Giga Press” die-cast front/rear body, combined with aluminium profile reinforcing beams.
Laser welding + bonding technology: enhancing the connection strength of aluminium profiles (solving the problem of easy deformation in aluminium welding).
Raw material fluctuations: the price of electrolytic aluminium is greatly affected by energy costs, and enterprises need to lock in long-term agreements.
Recycling system: establish a closed-loop recycling network (such as CATL’s cooperation with aluminium enterprises to recycle battery trays)
Multi-material hybrid design: aluminium profiles combined with carbon fiber and magnesium alloy (such as the aluminium-carbon hybrid body of the BMW iX).
Intelligent production: AI algorithms optimize the cross-sectional design of profiles to enhance material utilization.
Policy-driven: China’s “Technology roadmap for energy saving and new energy vehicles” requires that the aluminium consumption per vehicle reach 250kg by 2035 (with a target of 150kg for 2025).
The application of aluminium profiles in new energy vehicles has changed from “optional” to “mandatory”. In the future, with the advancement of integrated die-casting, recycled aluminium technology and high-end alloys, its penetration rate will continue to increase.


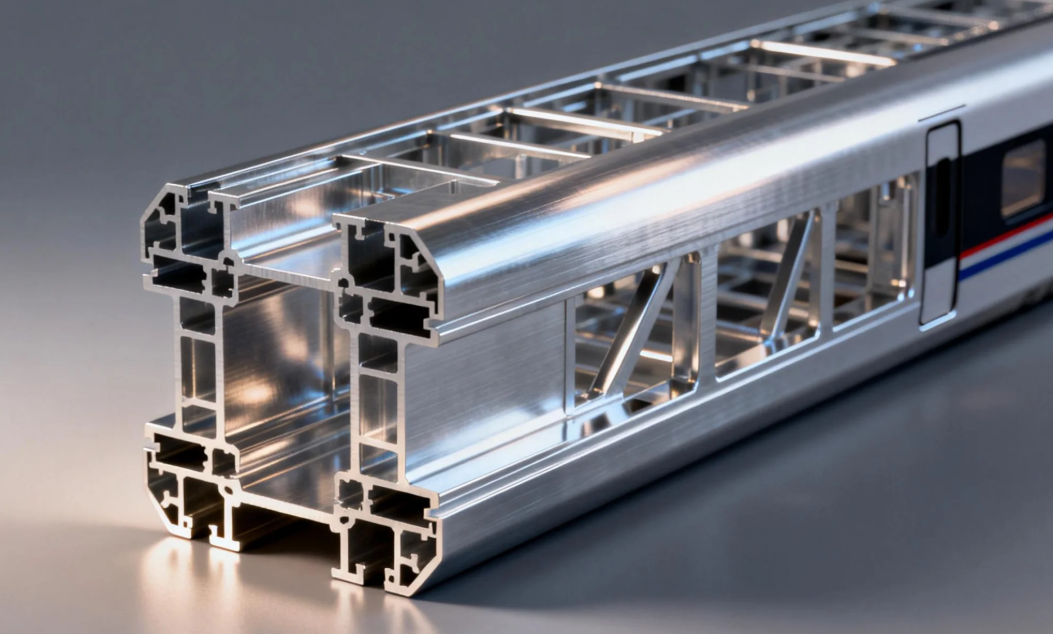
The advantages of using aluminium alloy for the main structure of high-speed train carriages

















Methods for distinguishing Indoor and Outdoor Aluminium Doors


Maintenance methods and tips for aluminium doors and windows

Characteristic of outward-opening and hung aluminium windows

Xinhe Aluminium Research: 7.14-7.18 Analysis of Aluminium Prices



Seven Benefits Of Using Aluminium Profiles In Curtain Wall Systems



The Composition and Application of Series 6 Aluminium Alloys


Top 5 Benefits of Using LED Aluminium Profiles in Modern Lighting

A Complete Guide to Aluminium Frame Profiles for Modern Structures



Exploring the Strength and Versatility of Aluminium Extrusion Profiles

How to Choose the Right Aluminium Profile Supplier for Your Project
